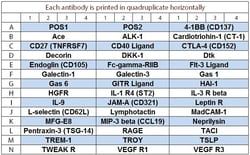
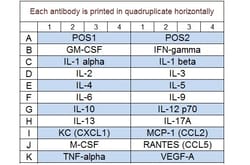
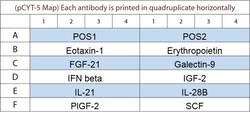
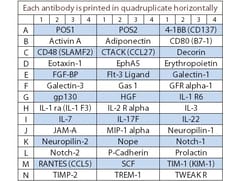
A combination of 5 non-overlapping arrays to quantitatively measure 50 Porcine cytokines. Suitable for all liquid sample types. Quantitative, Sandwich-based, Glass Slide Antibody Array. Simultaneous quantitative measurement of multiple proteins in a wide variety of sample types. Quantibody combines the high specificity and sensitivity of ELISA with the high throughput of the glass chip-based array. Less sample, more data: only 50 ul of sample is needed for quantification of up to 40 cytokines. Proteins detected: Angiopoietin-1, CCL3L1, Decorin, Eotaxin-1, Erythropoietin, FGF-21, Galectin-9, GASP-1, GM-CSF, IFN alpha, IFN-beta, IFN-gamma, IGF-2, IGFBP-5, IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-1 Ra, IL-10, IL-12 p70, IL-13, IL-15, IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-18, IL-21, IL-22, IL-28B, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, Insulin, IP-10, MCP-1, MIF, MIG, MIP-1 beta, NCAM-1, Osteoprotegerin, PDGF-BB, PECAM-1, PLGF-2, RANTES, SCF, TGF alpha, TGF beta 1, TIMP-1, TIMP-2, TNF alpha, TWEAK R, VEGF-A